The gut carries out trillions of microorganisms upon which digestion, immune function, and wellbeing depend. It will take some careful exercise on the part of the gut for you to maintain a good balance and lower chances of chronic diseases related to diabetes and inflammation, as follows: Feed it well, control stress well, create sleeping patterns, and keep well hydrated.
Key Points.
1. Eat Foods That Nourish Your Gut
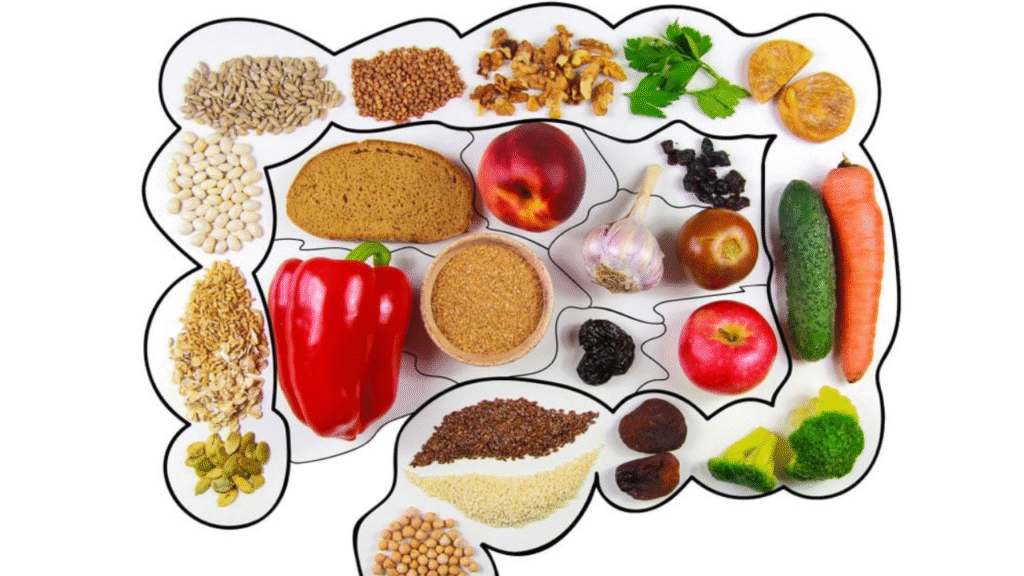
Whereas foods are critical in gut maintenance and healing, it turns out that non-inflammatory foods help greatly to make sure that the gut digests very well. Avoid those inflammatory foods such as fried foods, sweet foods, and the like.
Instead, foods that neutralize inflammation-the Mediterranean foods, mostly vegetables, fruits, whole grains, legumes, healthy fats-were reported to have generalizing effects in breaking down inflammatory environments and potentially helping gut health. This group of people has been said to harbor a larger diversity of gut microorganisms compared to those consuming sugary fatty foods.

2. Control Chronic Stress
Increased levels of stress have been shown to correlate with stomach dysfunctions, nausea, constipation, and diarrhea. An increase in the hormones that signal stress also raises the inflammation existing in your gut, providing the opportunity for greater bacterial imbalance.
Some of the techniques you could use to manage your stress include:
Deep breathing and meditation. Journaling. Time spent in nature. Relax, have a hobby. Expressing gratitude. Family and friends. Seven to nine hours of promising sleep. Physical activity for at least thirty minutes daily in something you enjoy. Good nutrition. Alcohol in moderation. Smoking cessation. You might also want to seek help from a therapist or support group.
3. Go Out: Every single day
Exercise is good for nearly everything, including gut health conditions. Having a regular physical exercise routine makes one free from chronic diseases: diabetes and obesity happen to be the most frequent ones. Exercisers have an increased number of bacteria in the gut as compared to those who do not do any exercise.
Before participating in any type of exercise program, speak to a health professional. However, adults need to engage in 150 minutes of moderate-intensity activity each week.
4. Sleep Well
It has been shown that reduced sleep can be a detrimental factor for good bacteria in the gut. An unhealthy gut is more likely to be the result of inflammation and predisposes one to chronic diseases.
Here are some of the easy tips you can use to try to sleep between seven and nine hours a night:
- Get a schedule and stick to it.
- Avoid all screens for at least an hour before sleep.
- The sleep environment should be cool and dark.
- If evening workouts disturb sleep patterns, then do not exercise in the late afternoon or during the evening.
5. Think Probiotics
For any gut well-being, any pre- or probiotic contact or maybe both deserve thought. Probiotics are living microorganisms for healthy repopulation of the gut with bacteria, whereas prebiotics nourish those good bugs.
Speak to your physician before beginning any supplemental changes. Naturally, high probiotic foods include fermented dairy products such as yogurt and foods like sauerkraut and kimchi.
6. Increase Water Intake
Hydration is easiest and best to boost gut health. A good amount of water consumption does affect the gut microbiome. Increased microbial diversity in the gut is good for gut health. On the flip side, it only aggravates inflammation and other chronic health conditions: Dehydration.
Keep a water bottle close at hand during the day, keeping it free with refreshing fruits or a splash of juice. Include high moisture content-watering and water-rich-from food, such as:
- Bell pepper
- Canteloup
- Cucumber
- Zucchini
- Watermelon
7. Talk With a Specialist
Some disorders of the gastrointestinal tract and food intolerances make up the symptoms of different poor gut health disorders. They are described by symptoms such as pain in the abdomen, disturbing gas, loose stools, nausea, and acid reflux. It may help a patient to find out by working with practitioners whether the body has sensations towards food or an intolerance to it.
Another part of the work is reviewing the medications the provider has a patient on and recommending changes when necessary. Some of the medicines that can cause harm to gut health include antibiotics (which cause alteration of microorganisms in the gastrointestinal tract) and proton pump inhibitors (which reduce the number of healthy bacteria in the gut.
8. Restrict Sugar
Sweet foods, including candies, pastries, ice cream, and the ubiquitous soda, create more inflammation of the gut and an imbalance in their microorganisms. Sugar-rich drinks include soda, energy drinks, juices, and sweetened teas or coffees.
Alcohol may harm gut health as it creates an imbalance of the gut microbiome. Hence, avoid or limit alcohol consumption.
9. Stop Smoking
Effects of smoking on health also include those of the gut, an impoverished variety of microorganisms in the gastrointestinal tract. Apart from this, both smoking of whether using cigarettes or electronic forms of smoking known as vaping, are associated with gut inflammation. Fortunately, by quitting smoking, you can reverse these effects.
Foods That Strengthen Gut Health
Feed your gut positively by consuming a whole, nutrient-dense diet to increase your nurturing levels and bring your microbiome into good equilibrium. Gut-health foods are:
- Berries
- Cherry
- Dark green leafy vegetables, mushrooms, broccoli
- Fermented foods (yogurt, fresh sauerkraut, kimchi, kefir, and kombucha)
- Oats
- Nuts, seeds
- Beans, lentils
- Whole grains
Signs of an Unhealthy Gut
You might be wondering what the signs of an unhealthy gut are. An imbalance, for instance, may most likely manifest the symptoms of
- Bloating
- Gas
- Constipation
- Diarrhoea
- Acid reflux
- Unintended weight changes
- Sleep disturbances
A lack of good bacteria in the gut may increase the risk for skin problems such as psoriasis and contribute to autoimmune diseases.
When Should You See a Healthcare Provider?
Concerns about gut health should lead one to visit a healthcare provider. Gastrointestinal symptoms such as constipation or the rare occasional bloated feeling are symptoms, but are not enough reason for one to visit a healthcare provider. Any person should visit a healthcare provider when those symptoms appear nearly daily and do not improve over time.
The healthcare provider typically conducts a thorough physical examination and asks several questions to clarify the symptoms and the history of health. He or she may request diagnostic tests, including blood tests.
Key Takeaways
- Gut health definition is a kind of ratio of beneficial to harmful microorganisms in your gastrointestinal system, characterized by various symptoms such as constipation, gas, diarrhea, nausea, or heartburn.
- Your gut can also switch to the best by food, water, exercise, sleep, relative stress management, and the most importantly, healthy habits.
- Otherwise, have the health professional explain some more when things do not seem to work as they should be serving the desired purpose.
Conclusion:
The slow and underdeveloped scientific understanding has also led to misconceptions about gut health. These nine daily habits will really make a difference in your digestive system and overall balance in your body. These changes may appear trivial-for example, considered conscious eating, drinking more water, or leading a diet that’s friendly to the gut-but they come together to create a truly powerful effect. The key focus is not a precise definition; rather, consistency is what will bring long-term change through daily little efforts to a gut that will start taking you to realms of better health, well-being, and vitality.
FAQs:
Why is gut health important?
Gut health supports digestion, strengthens immunity, boosts energy, and maintains balance in overall physical and mental well-being.
How can I naturally improve my gut health daily?
Eat fiber-rich foods, stay hydrated, manage stress, sleep well, and include probiotics for a balanced digestive system.
Can poor gut health affect mental health?
Yes, poor gut health can disrupt the gut-brain connection, leading to mood changes, anxiety, or reduced mental clarity.
What foods are best for gut health?
Fermented foods, probiotics, fiber-rich fruits, vegetables, and whole grains help nourish good bacteria and improve digestion.
How long does it take to see gut health improvements?
With consistent healthy habits, noticeable improvements in digestion and energy levels usually appear within a few weeks to months.
Medical Disclaimer
The information provided on Health Tips India is intended for educational and informational purposes only. It should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
Always consult a qualified healthcare professional before making any health-related decisions or changes to your diet, exercise, or medical routine.
SamhithaHealth & Wellness Content Writer
a Health & Wellness Content Writer with over 6 years of experience creating research-based health articles. She specializes in nutrition, weight management, diabetes care, skin health, and healthy lifestyle practices. Here content is carefully written using trusted medical and scientific sources to ensure accuracy and clarity for readers.