Liver cancer, mainly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), is a serious health concern in India. It often develops silently in its early stages, making early detection crucial for better outcomes. Many people ignore subtle signs until the disease advances, reducing treatment success.
In India, liver cancer cases are rising due to changing lifestyles, increasing obesity, diabetes, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), alongside traditional risks like hepatitis and alcohol use. According to recent data, the age-adjusted incidence rate of HCC in India ranges from 4 to 7.5 per 100,000 for men and 1.2 to 2.2 for women, with a male-to-female ratio of 4:1. The disease typically appears between ages 40 and 70.
This comprehensive guide covers early liver cancer symptoms, risk factors specific to India, causes, prevention, screening, and when to see a doctor. Recognizing these signs early can save lives.

What is Liver Cancer?
Liver cancer starts in the liver cells. The most common type is hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), accounting for over 90% of cases. It often develops in livers damaged by chronic conditions like cirrhosis (scarring).
The liver, located in the upper right abdomen, filters blood, produces bile, and detoxifies substances. When cancer forms, it disrupts these functions, leading to symptoms.
In early stages, liver cancer may show no symptoms, which is why it’s called a “silent killer.” As it progresses, signs become noticeable.


Early Symptoms of Liver Cancer
Early liver cancer symptoms are often vague and mimic other conditions like indigestion or fatigue. Don’t ignore persistent signs, especially with risk factors.
Here are the most common early symptoms:
- Unexplained Weight Loss Sudden weight loss without diet or exercise changes is a red flag. Cancer cells use energy, and reduced appetite contributes.
- Loss of Appetite and Feeling Full Quickly You may feel full after small meals (early satiety) due to tumor pressure or liver dysfunction.
- Abdominal Pain or Discomfort Pain in the upper right abdomen, where the liver sits, is common. It may feel dull or sharp and sometimes extends to the shoulder.

A young man has abdominal pain in the liver area that has fatty …
- Fatigue and Weakness Persistent tiredness not relieved by rest affects daily life.
- Jaundice (Yellowing of Skin and Eyes) Yellow skin, eyes, or dark urine occurs when the liver can’t process bilirubin. Itching may accompany this.
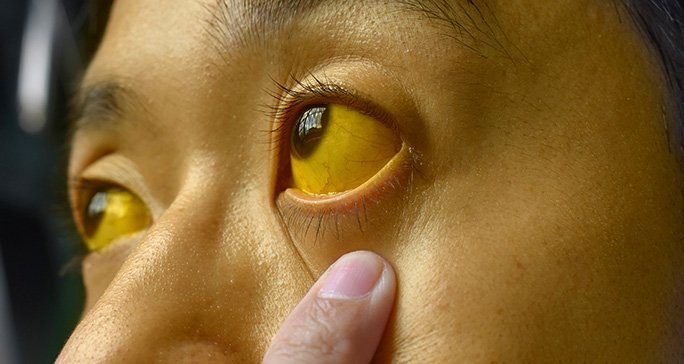
What causes jaundice in adults? | MD Anderson Cancer Center
- Abdominal Swelling or Bloating Fluid buildup (ascites) causes swelling. The abdomen may feel firm.
- Nausea and Vomiting Ongoing nausea disrupts eating and worsens weight loss.
- Fever and Sweating Low-grade fever or night sweats may occur.
Other less common signs include pale stools, bruising easily, or a palpable lump.
If symptoms last over two weeks, consult a doctor immediately.
Risk Factors for Liver Cancer in India
India’s liver cancer burden shifts from viral hepatitis to metabolic issues.
Key risk factors:
- Chronic Hepatitis B or C — Major causes, often from unsafe injections or blood transfusions. Hepatitis B vaccination reduces risk.
- Alcohol Consumption — Heavy drinking leads to alcoholic liver disease and cirrhosis.
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD/MASLD) — Rising with obesity and diabetes; now a leading cause.
- Cirrhosis — From any cause, scar tissue raises cancer risk.
- Obesity and Diabetes — Linked to NAFLD.
- Aflatoxin Exposure — Toxins in contaminated food like peanuts.
- Smoking — Increases risk, especially with other factors.
Men face higher risk than women, with peak ages 40-70.
Causes and How Liver Cancer Develops
Liver cancer usually arises from chronic damage:
- Infection (hepatitis) or toxins (alcohol) inflame the liver.
- Inflammation causes scarring (cirrhosis).
- Scarred cells mutate into cancer.
In some cases, like hepatitis B, cancer develops without full cirrhosis.
Prevention of Liver Cancer in India
Prevention focuses on reducing risk factors:
- Get vaccinated against Hepatitis B (included in India’s immunization program).
- Screen blood and practice safe injections to avoid Hepatitis C.
- Limit alcohol (or avoid it).
- Maintain healthy weight through diet and exercise to prevent NAFLD.
- Eat balanced diet; avoid moldy grains.
- Quit smoking.
- Manage diabetes.
Screening and Early Detection Guidelines in India
Early detection improves survival. Indian guidelines (INASL) recommend:
- High-risk individuals (cirrhosis, chronic hepatitis) undergo surveillance every 6 months.
- Use abdominal ultrasound, with or without AFP blood test.
- High-risk groups: Cirrhosis patients, chronic HBV/HCV, family history.
Consult a gastroenterologist or hepatologist for screening.
When to See a Doctor
See a doctor if you have:
- Persistent abdominal pain
- Unexplained weight loss
- Jaundice
- Fatigue
- Swelling
Especially with risk factors like hepatitis, alcohol use, or fatty liver.
Early diagnosis via ultrasound, CT/MRI, or biopsy enables treatments like surgery or transplant.
Conclusion
Liver cancer is rising in India due to metabolic diseases and traditional risks. Early symptoms like weight loss, abdominal pain, and jaundice are subtle but critical. Ignoring them can lead to advanced disease.
Prioritize prevention through vaccination, healthy lifestyle, and moderation. High-risk individuals need regular screening.
If you notice signs, seek medical help promptly. Early action saves lives.
(Word count: approximately 1520)
Disclaimer: This information is educational; consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice. Sources include Mayo Clinic, Cleveland Clinic, INASL guidelines, and recent epidemiological data.
SamhithaHealth & Wellness Content Writer
a Health & Wellness Content Writer with over 6 years of experience creating research-based health articles. She specializes in nutrition, weight management, diabetes care, skin health, and healthy lifestyle practices. Here content is carefully written using trusted medical and scientific sources to ensure accuracy and clarity for readers.

